
Interpreting the Collision Cross Sections of Native-Like Protein Ions: Insights from Cation-to-Anion Proton-Transfer Reactions. Kenneth J. Laszlo, Matthew F. Bush. Anal. Chem. 2017, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01474. (Link)
The effects of charge state on structures of native-like cations of serum albumin, streptavidin, avidin, and alcohol dehydrogenase were probed using cation-to-anion proton-transfer reactions (CAPTR), ion mobility, mass spectrometry, and complementary energy-dependent experiments. The CAPTR products all have collision cross-section (Ω) values that are within 5.5% of the original precursor cations. The first CAPTR event for each precursor yields products Continue reading “New Publication: Interpreting the Collision Cross Sections of Native-Like Protein Ions: Insights from Cation-to-Anion Proton-Transfer Reactions”
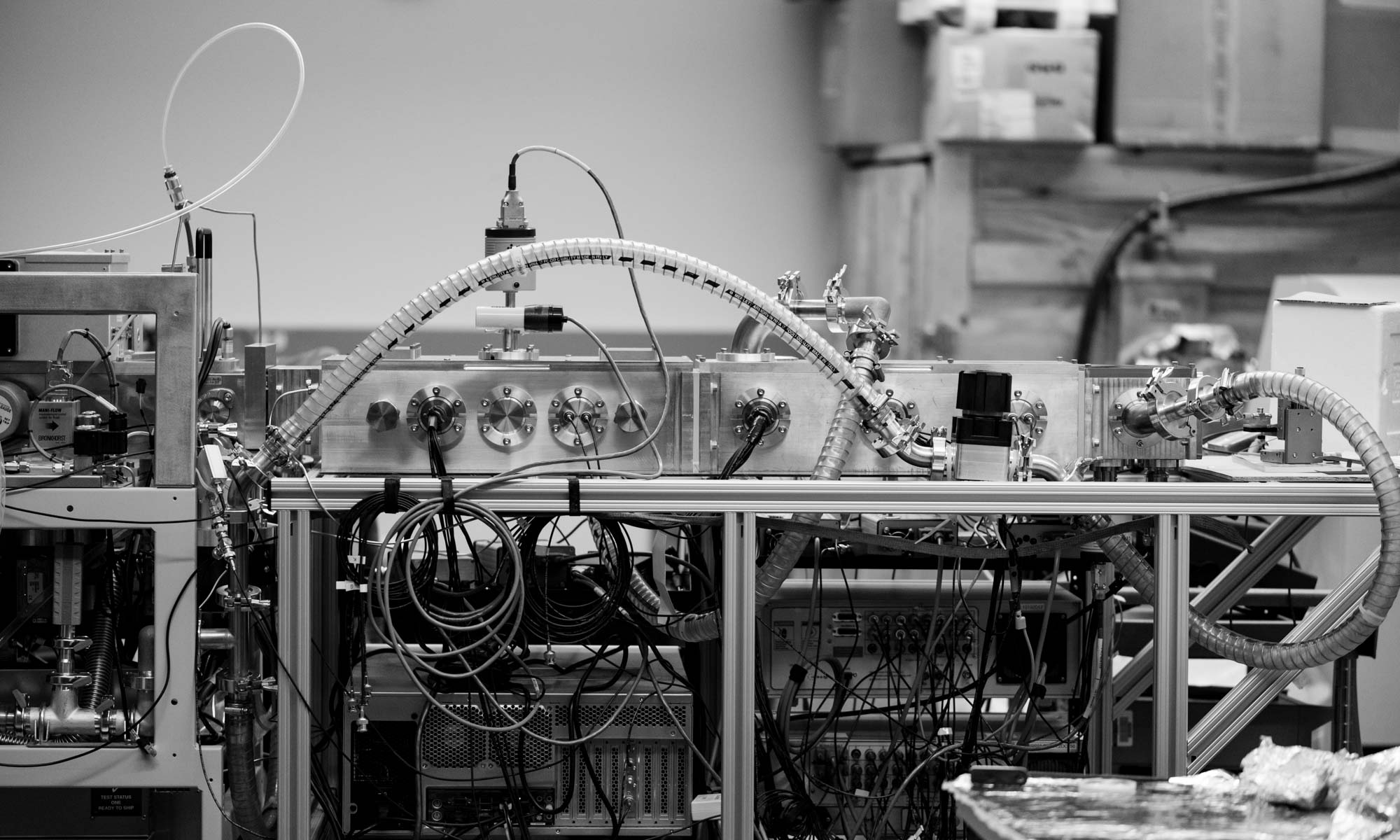
 Structural Dynamics of Native-Like Ions in the Gas Phase: Results from Tandem Ion Mobility of Cytochrome c. Samuel J. Allen, Rachel M. Eaton, Matthew F. Bush. Anal. Chem. 2017, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01234. (
Structural Dynamics of Native-Like Ions in the Gas Phase: Results from Tandem Ion Mobility of Cytochrome c. Samuel J. Allen, Rachel M. Eaton, Matthew F. Bush. Anal. Chem. 2017, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01234. (
 Effects of Solution Structure on the Folding of Lysozyme Ions in the Gas-Phase. Kenneth J. Laszlo, Eleanor B. Munger, Matthew F. Bush. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 2759–2766. (
Effects of Solution Structure on the Folding of Lysozyme Ions in the Gas-Phase. Kenneth J. Laszlo, Eleanor B. Munger, Matthew F. Bush. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 2759–2766. ( Julia Greenwald, a first year graduate student in the Bush Lab, was recently awarded a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship! From the NSF:
Julia Greenwald, a first year graduate student in the Bush Lab, was recently awarded a National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship! From the NSF:
 Prof. Bush has been named the recipient of the 2017 Arthur F. Findeis Award for Achievements by a Young Analytical Scientist. The Findeis Award is given annually by the American Chemistry Society Division of Analytical Chemistry, to recognize and encourage outstanding contributions to the fields of analytical chemistry by a young analytical scientist. The award will be presented at the 254th ACS National Meeting to be held August 20-24, 2017 in Washington DC. (
Prof. Bush has been named the recipient of the 2017 Arthur F. Findeis Award for Achievements by a Young Analytical Scientist. The Findeis Award is given annually by the American Chemistry Society Division of Analytical Chemistry, to recognize and encourage outstanding contributions to the fields of analytical chemistry by a young analytical scientist. The award will be presented at the 254th ACS National Meeting to be held August 20-24, 2017 in Washington DC. (
 The Bush Lab welcomes Daniele Canzani! Click
The Bush Lab welcomes Daniele Canzani! Click  Effects of drift gas selection on the ambient-temperature, ion mobility mass spectrometry analysis of amino acids. Kimberly L. Davidson and Matthew F. Bush. Anal. Chem. 2017, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04605. (
Effects of drift gas selection on the ambient-temperature, ion mobility mass spectrometry analysis of amino acids. Kimberly L. Davidson and Matthew F. Bush. Anal. Chem. 2017, DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04605. (
You must be logged in to post a comment.